Research Articles
1. Yang, Yajing; Yang, Jiye; Li, Fenglin; Sun, Dayin; Zhu, Jintao; Nie, Zhihong; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Stepwise Grafting of Polymer Single Chains onto Nanoparticles, Macromolecules, 2025, 58, 1256-1264.
It is important to design hierarchically structured functional polymer/inorganic composite nanoparticles (NPs) and self-organize them toward programmable superstructures thereby. We propose the synthetic approach of stepwise grafting anionic polymer single chains onto functional nanoparticles via termination, which is ensured by the strong steric hindrance effect of the grafted chains to the target chains with a comparable size. The concept is demonstrated by the precision synthesis of NP-inserted diblock copolymer analogies of PVSt-b-PmSt-[Fe3O4@SiO2]-PMMA-b-PtBA with two different polymer single chains at the opposite sides (PVSt-b-PmSt: poly(4-vinylphenyl-1-butene)-block-poly(4-methylstyrene), PMMA-b-PtBA: poly(methylmethacrylate)-block-poly(tert-butyl acrylate)). Both end segments of PVSt and PtBA are reactive to derive functional groups such as amino and carboxylic acids by the orthogonal clicking reaction and hydrolysis. The functional groups allow visualization of the composite NPs by stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy upon selective fluorescence dyeing and the self-organization by specific interactions toward superstructures at varied pHs. The approach is valid for the stepwise grafting of six single chains of varied compositions along the three-dimensional coordinate. The composite NPs with defined numbers and types of functional groups, and thus interaction directions, provide a huge platform for diversifying superstructures, especially under external fields.
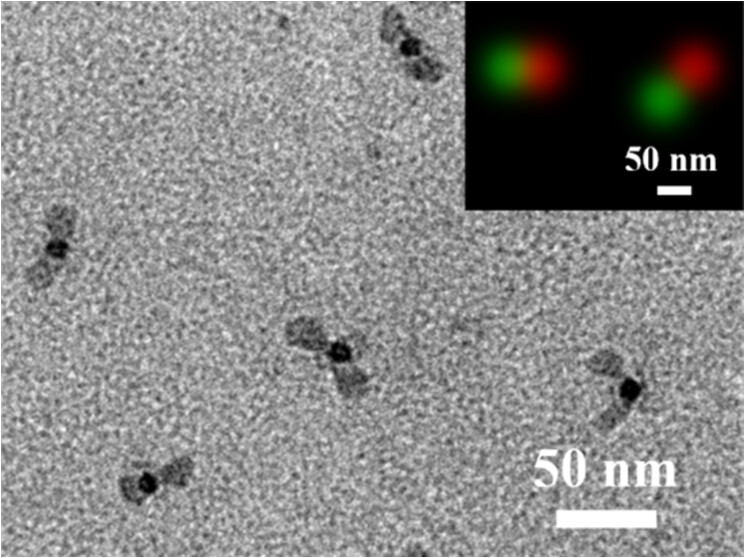
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.4c03032
2. Li, Fenglin; Yang, Yajing; Sun, Dayin; Ye, Yilan; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Scalable synthesis of Janus single-chain/nanoparticle hybrids. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2025, 56(1), 114-123.
Asymmetric polymer single-chain@nanoparticle hybrids demonstrate fine microstructures and synergetic performances, which serve as important building blocks toward functional materials. It is crucial to develop methodologies for the large-scale preparation of hierarchically structured functional hybrids. Starting from the triblock bottlebrush polymers, Janus nanoparticles composed of Fe3O4 are synthesized on a large scale through electrostatic-mediated intramolecular crosslinking, involving coordination with metallic ions at the central region, which is rich in PVP side chains at a high concentration of 150 mg/mL. Shape of the nanoparticles is controllable from spherical to ellipsoidal by alteration of the length ratio of the backbone and the grafting side chain. PVSt and PBBzSt blocks at the opposite ends of the nanoparticle could be modified orthogonally to derive amino- or (and) carboxylic acid groups. AB type Janus nanoparticles are thus derived, which are able to self- assembly into diverge superstructures upon alteration of pH values. The self-assembly and the superstructures could be easily visualized under stimulated emission depletion microscope (STED) upon fluorescent dyeing the functional groups. A layer of SiO2 is formed at the Fe3O4 NP by the sol-gel process, and bromopropyl- groups are further introduced by using the silane. At the Janus composite nanoparticle, single-chains could be sequentially grafted by steric hindrance assisted termination of living anionic polymer single-chains with tunable composition and microstructure. The Janus composite nanoparticles bearing four different polymer chains display multivalent directional interactions, which are promising to self-assembly functional superstructures.
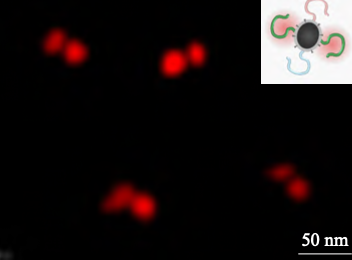
https://doi.org/10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2024.24173
3. Li, Fenglin; Wen, Zhendong; Yang, Yajing; Sun, Dayin; Zhu, Jintao; Nie, Zhihong; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Large-Scale Synthesis of Janus Nanorods by Electrostatics-Mediated Intramolecular Cross-Linking of Polymeric Bottlebrushes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2025, 147, 6857-6865.
Nanorods are promising to construct functional superstructures. The currently used nanorods are essentially symmetric, with the same materials at the ends. Theoretical prediction indicates that asymmetric Janus nanorods with varied materials at the ends are advantageous in the synthesis of diversified functional self-assembled materials. Herein, we propose a novel method of electrostatics-mediated intramolecular cross-linking of Janus polymer bottlebrushes to synthesize large-scale asymmetric Janus nanorods at an unprecedentedly high concentration of 300 mg/mL. Compositions of both the nanorod body and ends are broadly tunable in an orthogonal mode to endow the nanorod functional groups for self-assembly, which could be visualized under a STED microscope upon dyeing. The sample amino acid analogous Janus nanorods are achieved by the orthogonal hydrolysis and click reaction at the opposite ends, serving as building blocks to self-organize into superstructures from linear wires, branches, and networks that are highly dependent on the valence states.
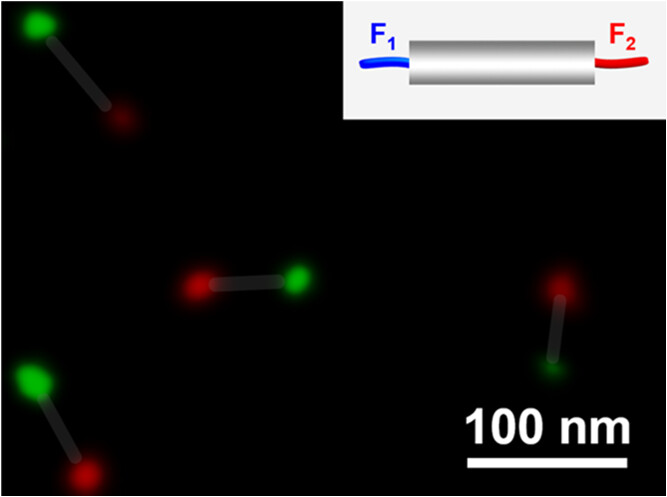
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c16990
4. Huo, Lujie; Qu, Kairu; Yang, Zhenzhong; Jia, Di*. Dynamics of Charged Ring Polymers under Gel Confinement. Chinese J. Polym. Sci., 2025, 43, 399-405
Ring polymers are ubiquitous in various fields including biomaterials, drug release and gene therapy. All of these applications involve the dynamics and diffusion process of ring polymers in a confined environment. By using dynamic light scattering (DLS), we discovered a dynamical transition for charged ring polymers with increasing ring concentration in the gel matrix from a diffusive state to a non-diffusive topological frustrated state with a more compact conformation. When the ring polymer size is smaller than the mesh size of the gel matrix, the rings are diffusive at low concentration of 5 g/L. The ring diffusion coefficient in the gel matrix is an order of magnitude smaller than that of rings in solution, obeying the Ogston’s model. At high ring concentration of 40 g/L, the collective dynamical behavior of the charged rings exhibits a topologically frustrated non-diffusive state, which may originate from the inter-ring threading with the external confinement from the gel matrix. Based on our previous theoretical work, we also conjectured that in such a non-diffusive state, the ring polymers might adopt a more compact conformation with the overall size exponent v=1/3.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-025-3291-0
5. Qu, Kairu; Du, Linhan; Zhou, Shuqi; Huo, Lujie; Gu, Anqi; Lu, Diannan; Chen, Chunlai; Jia, Di; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Large-Scale Synthesis of Polymer Rings by Electrostatic-Mediated Closure of Single-Chain Nanoparticles. Macromolecules, 2025, 58, 4131-4137.
Polymer rings are unique over their linear counterparts in fundamental and engineering aspects. Although ring closure of polymers is a proven general method toward rings, the large-scale synthesis in concentrated solutions remains challenging due to the concurrent intermolecular reactions. Herein, we propose the electrostatic-mediated ring closure of polymers in the dynamic single-chain nanoparticle (SCNP) globular state, enabling large-scale synthesis of highly pure polymer rings at an unprecedentedly high concentration of 150 mg/mL. The dynamic SCNPs are also achieved by the electrostatic-mediated intramolecular cross-linking of polymers in concentrated solutions. Poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA)-based telechelic polymers are selected to demonstrate the concept. The charged dynamic SCNPs are constructed by simple amine-acid-specific interactions, and thiol–ene and Diels–Alder click reactions are employed for the ring closure to demonstrate the generality. The microstructure and composition of the rings can be tuned from the corresponding polymers with varied segmental sequences and compositions. The topology and function can be further tuned by the favorable growth of functional materials at the desired sites of the polymer rings.
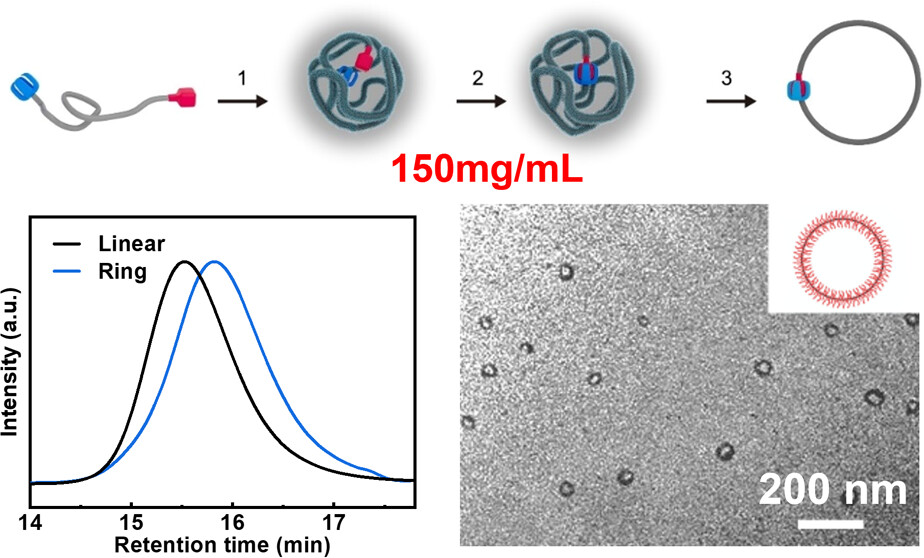
6. Yang, Jiye; Sun, Dayin; Gu, Anqi; Wen, Zhendong; Wang, yan; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Scavenger Resin Enabling Simplification of Complicated Living Anionic Polymerization. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater., 2025, 7, 6493-6499.
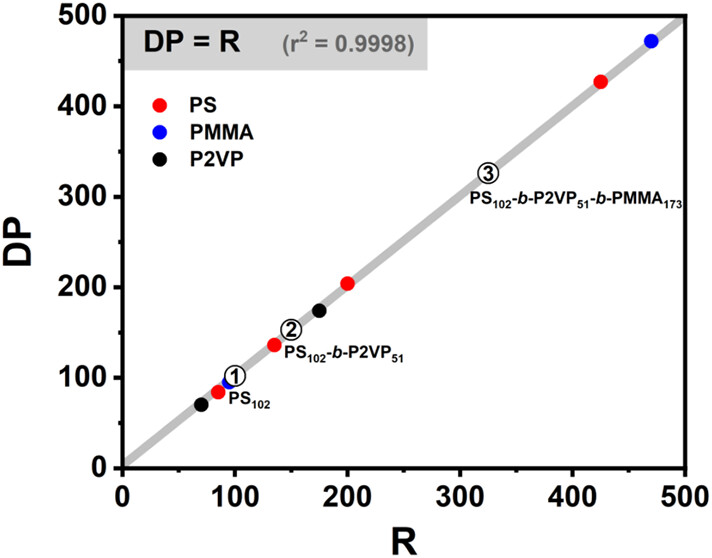
Since Szwarc first proposed living anionic polymerization in Nature (1956), this method has proven to be the most powerful approach for large-scale synthesis of nearly uniform polymers with tunable compositions and microstructures. Eliminating various impurities toward the absolute purification of reagents and vessels is a prerequisite for living polymerization. Conventional purification methods are laborious and highly specific for the reagents, significantly limiting the potential of the anionic polymerization. Herein, we develop a facile and universal purification method by the anionic initiating scavenger resin that eliminates impurities via self-sacrificial reactions, substantially simplifying the process. For representative synthesized homopolymers, the degree of polymerization (DP) shows a strict linear correlation with monomer/initiator molar ratios (R) according to DP = R while maintaining low dispersity indices (Đ ≈ 1.03). The living anionic polymerization also enables scalable production of nearly uniform copolymers through designed one-batch sequential polymerization. This large-scale synthesis of composition-controlled polymers with a narrow distribution advances the fundamental understanding of structure-performance relationships and supports the precise construction of uniform self-assembled nanostructures.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.5c00954